Do you want your website to stay ahead of the competition in Google search results? Or do you want to find out how to improve website performance?
Why you’re finding competitors and can’t find your website when you type for a term for your potential customers?
Let us help you! If you are looking for an SEO checklist that will help you to improve your website’s organic traffic, you have just found it. And, just a tip – don’t forget to get dofollow backlinks or buy backlinks to improve your SEO score..
Yes… organic traffic. Great! Aside from being able to define SEO as a set of techniques that rank websites better within Google search results, SEO is much more than that.
Quality SEO, one might say, is one of the most effective ways to improve website performance and create greater value.
Search engine optimization is a long-term process that needs to be approached very carefully, smartly, and strategically. Depending on your choices, Google decides whether you deserve to appear on the first page of search results or not.
So let’s start with SEO fundamentals.
SEO In a Nutshell
Applied knowledge on how search engines crawl and index websites + Applied knowledge on how Google ranks websites = A high-ranking site and lots of valuable traffic.

Here are the main categories we want to cover when we do the ultimate guide:
- The theory of good SEO
- Technical SEO checklist
- A keyword research checklist
- On-page SEO and content checklist
- Off-page SEO checklist
1. The Theory of Good SEO
Common practices to have a well-performing SEO site:
- Website analysis and development
- Keyword research
- Usability, user experience, and content
- Popularity and links
- Not to do’s
- Measurement
1.1. Website Analysis and Development
Search engines are smart but not that smart, so you need to help them find your content, common issues may be:
- Content behind forms
With all this investment in content, is it better to leave content free or lock it behind forms in order to generate leads?
Free content gets 20 to 50 times more downloads than content that requires the visitor to fill a form with their contact information to gain access (i.e. “locked” content).
The locked content is not only unavailable to online visitors, but it also locks out search engines. The more free content you have, the more pages and content engines can index – potentially improving your search rankings and traffic.
- Duplicate pages (canonical tags)
If you have a single page accessible by multiple URLs, or different pages with similar content (example: a page with both a mobile and a desktop version).
Google sees these as duplicate versions of the same page. Google will choose one URL as the canonical version and crawl that, and all other URLs will be considered duplicate URLs and crawled less often.
- Erroneous crawling directives (robots.txt, noindex)
The robots.txt file is one of the main ways of telling a search engine where it can and can’t go on your website (crawl page on the website).
All major search engines support the basic functionality it offers, but some of them respond to some extra rules which can be useful too.
Noindex on the other hand tells the bots which pages they should or shouldn’t index. This is especially useful for testing pages or A/B testing, but also for keeping those not-so-important pages on your website away from the scrutiny of Google.
- Keyword issues
Keywords have to be consistent. So, you must use keywords ‘sensibly’ in URLs, headings, navigation & content, and utilize descriptive keyword phrases in the URLs when possible.
Also, your keywords should be in the title (shown at top of the page in the browser), headings (H1, H2, H3), and finally, use your keywords in your content.
When Google sees the same (or related) keywords all throughout, it understands the subject of your content and the focus of your website.
If you write keywords related to SEO tips in your page title, but then go on and talks about a completely different topic in your content, Google will mark your site as irrelevant and downrank you.
So, be consistent and be natural, don’t stuff your keywords just for the sake of having them.
- Write a good attractive meta description
Meta descriptions show below the title in the search engine result pages and are the first contact with both search engine bots and users.
A relevant meta description will win you points with the Google bits, and a catchy meta description can provide a higher click-through rate (CTR).
- Make sure your pages are indexed
In simple terms, make sure your most important content is indexable, in HTML format, and you do not use unsupported technologies like Flash.
Also, use HTML tags such as alt texts for images, the proper heading hierarchy, crawlable and hierarchical link structure, etc.
- Use proper hierarchy
Speaking of hierarchy, make sure you place important content high in the site hierarchy, make it is accessible to search engines, use canonical URL tags for duplicate content and keep it consistent.
Headings (H1, H2, H3) show bots the hierarchy of your text, so use them wisely. Never use more than one H1 per page, so instead, use H2 and H3 to highlight main headings and subheadings.
- Use no-follow links to avoid “link farming” a.k.a. placing too many links on a page and being marked as a backlink farming website.
- Keep page load times to a minimum
1.2. Choose the Correct Keywords
First ask yourself if you were looking for the information, product, or service your website provides, what would you type into Google?
Type those phrases into Google, do those queries return sites similar to yours? Are they high-demand keywords?
Use tools like Google Keyword Planner to check volumes, level of demand and to find other relevant keywords and phrases.
1.3. Great Usability and Content
Search engines look for signals to identify how successful they have been in ‘recommending pages’, these signals include bounce rate, repeat searches, and time between searches.
Transmit ‘what’s the page all about’ clearly and prominently, tell the user they are in the right place for what they need.
Deliver quality content that delivers what was promised in the title and meta description texts.
Create content that engages and encourages user interaction and consideration, content that matches the search intent of the user, so transactional, informational, or navigational.
1.4. Earn Popularity and Links
Search engines see links as recommendations, but they also gauge the quality of the recommendation, domain and page authority are increasingly important, as is relevancy.
Anchor texts are important, but they need to be natural. If everyone says the same thing about you it looks suspicious, yes? The same applies to content.
Fresh content and links are essential and “past glory: counts for little on the web. You need to be relevant today.
Social signals are also important. Even though search engines may not consider them directly, they provide trust, engagement, and links.
1.5. Earn (don’t “buy”) Links
Provide value in the form of fun or valuable content and people will link to your site and recommend you to their peers.
- Be newsworthy, do interesting things, create great research, be in the right place with the right people, enter the right competitions;
- Create content people will want to borrow, steal or share, place it in “public” places like forums and social platforms, and have it link back to your site;
- Get reputable customers, partners, or suppliers to link to you;
- Be listed (where relevant) in high trust-directories.
1.6. Summing up the “Don’ts” List
- Don’t create low-value content with endless blog post tags and meta tags
Quality over quantity is essential in your every SEO decision. High-quality content, links, and meta tags will ensure a higher CTR, a higher rank, and a better reputation with your users.
- Don’t stuff keywords into content in the belief that the more times you mention a keyword the better
Keywords are what get your content ranked and visible. Too many repetitions and you risk getting downranked for keywords stuffing.
You also risk creating what is called “keyword cannibalism” where several of your own pages compete with each other.
So, be consistent, but also be creative. Use related keywords to show you keep with one topic instead of copying the same ones over and over again.
- Don’t ignore the long tail and don’t fixate on a few high volumes, high demand keywords
Longtail keywords are more natural for users. Instead of using general keywords like “SEO”, use something your users actually look for in search engines, like “How to do good SEO”.
Also, use tools like Google keywords and Ubersugget to see the search volume, search difficulty, and related examples of your keywords and aim for those with high search volume but low search difficulty.
These keywords are the ones people are searching for, but not many sites provide the content for it. And that’s where you want to be – your niche.
- Don’t get links on irrelevant and low-quality sites and directories, don’t do link exchanges or buy links
Link buying and link exchanging is a practice that has been around since the first version of the Google algorithms. This also means Google is on to you.
If Google sees that you and a group of other sites are always linking to each other, especially if it’s irrelevant to you and your niche, you will get punished.
So, earn your keywords, don’t buy them.
- Don’t use cloaking to fool search engines and don’t copy content
If you keep up with the Google algorithm news, you know that duplicated content is no longer punished with downranking, and you might think you can steal someone else’s work and claim it as your own.
But, in reality, duplicated content today simply doesn’t get ranked. So, if you do copy other people’s content, you simply won’t show up on Google.
Be unique.
- Don’t get a Google Penalty
That is the ultimate goal – don’t get on Google’s naughty list. Keep up with your content and follow the rules and you will be fine.
Ranking is slow and tedious, but it is nothing compared to re-gaining Google’s and your users’ trust.
2. Technical SEO Checklist
Technical SEO is a series of procedures of a technical nature by which you adapt your website for search engines and browsers so that they can load and index it correctly and quickly, and so that they can see exactly what content is on it.
Well done technical SEO is the first and mandatory step in how to improve website optimization for search engines.
Read suggestions on how to do this below:
2.1. Sign up for the Google Search Console
 The Search Console is a website checker, a place where you can track how your site “breathes”, identify problems related to it, and track backlinks.
The Search Console is a website checker, a place where you can track how your site “breathes”, identify problems related to it, and track backlinks.
These are the key things you need to set up and monitor regularly:
- Preferred domain: Set how your site appears in search results with or without the www prefix
HTML enhancements: this is where the Search Console will recommend any meta description and title enhancements and notify you of non-indexable content - Links to your website: Here you can see which domains are linking to your website
International targeting: Make sure you’re targeting your preferred audience based on language and country - Indexing Status: This allows you to find out how many pages are currently indexed. You can also see all the pages that the robots have blocked or removed
- txt editor: here you can edit robots.txt and check for errors
2.2. Subscribe to Google Analytics
 Google Analytics is free software that you can use to track traffic to your website. Track the demographics of website visitors, the performance of a particular campaign, and how long people stay on your website.
Google Analytics is free software that you can use to track traffic to your website. Track the demographics of website visitors, the performance of a particular campaign, and how long people stay on your website.
2.3. Website Speed Test
Use the website speed test tool to see how fast your website is loading, then implement the changes it recommends.
2.4. The Website Must be Responsible
Your website and its content must be optimized for any screen or device size. Keep in mind that Google has stated that responsive design is the best way to optimize for mobile phones.
2.5. Optimize the Target Titles
- You should have 50 to 60 characters, including spaces
- The most important keywords must be first in the title
- If your business name is not part of the relevant keywords, put it at the end of the title
- Do not duplicate titles, they must be written differently for each page
- Meta titles must accurately describe the content on the page
- Don’t overdo it with keywords
- The main title of the web page (<h1> tag) must be different from the meta title
2.6. Adjust the Meta Description
- Make sure the meta description contains the most important keyword for each page
- Write a legible and clear text
- The meta description should not be longer than 135 to 160 characters. Either way, search engines will break the end of the text, so make sure the keywords are important in the visible part of the description.
- Do not duplicate meta descriptions
2.7. Write Good Titles
The titles of individual pages should be less than 55 characters to ensure their full visibility on the SERPs. Make sure they are appealing and that they describe well what is on the website.
2.8. Check the HTML Tags
 Make sure the titles are labeled H1 and any subheadings in your articles are labeled H2, H3, etc. They are used in descending, logical order.
Make sure the titles are labeled H1 and any subheadings in your articles are labeled H2, H3, etc. They are used in descending, logical order.
2.9. Optimize your Media Files
Make sure your images are optimized for the web. That they are not too big and do not slow down the website. It is good to mark images with alt-text correctly.
2.10. XML / HTML Sitemap
Make sure your website has an accurate sitemap in XML and HTML format to ensure thorough indexing by Google.
2.11. Security SSL / TLS Protocol
 The SSL / TLS protocol ensures that all communication between the browser and the website is encrypted. HTTPS is often used to protect highly confidential online transactions, such as online banking and order forms. If transactions are performed on your website, it is advisable to implement the SSL / TSL protocol.
The SSL / TLS protocol ensures that all communication between the browser and the website is encrypted. HTTPS is often used to protect highly confidential online transactions, such as online banking and order forms. If transactions are performed on your website, it is advisable to implement the SSL / TSL protocol.
2.12. Duplicated Content
If you have identical content across multiple webpages, set 301 redirects so that Google only indexes the page you want.
Make sure that Google indexes only the desired domain, i.e. with or without the www prefix. Google may treat the www and non-www versions as separate websites, and this may harm your visibility.
If you post the same content from another site (with permission, of course), use the rel = canonical tag on each page that links to the original website.
2.13. Nofollow Tag
Add a rel = “no-follow” tag to all links you don’t want search engines to index, such as sponsored content.
2.14. Errors
It is necessary to thoroughly investigate whether there is an error 400, 403, 404, 500, and 503 on the website. If you see more than 404 errors from internal links, fix them immediately.
Make sure you use redirect 301 for redirection and avoid redirects 302 and 307.
2.15. Internal Link Structure
3. A Keyword Research Checklist

We believe we shouldn’t spend too much highlighting the importance of keyword research in SEO.
Without cleverly defined keywords it doesn’t work. Make no mistake – keyword research for a website is a demanding and often tedious job.
3.1. Make a List of Relevant Topics
Roll out your research and consider which topics or categories you would like to rank for using generic keywords.
Remember what you know about the company so far and come up with about 10 topics that describe its business. In the next steps, you will fill in these topics with specific keywords.
In this step, it is important to put yourself in the shoes of your buyer personas, that is, think about which topics they will search for, and for which they want to find you on the search engine.
3.2. Fill in the Topics with Keywords
Now that you have a few topics to focus on when researching, it’s time to determine which keywords to use for each topic.
The keywords listed are those terms that you think users type in when searching. For these terms, your goal is to rank as high as possible in the SERP.Do this for all the topics you defined in Step 1.
E.g. for the “SEO” topic, the keyword list would look like this:
- how to do SEO analysis,
- search engine optimization,
- SEO search engine optimization,
- how to rank on search engines,
- elements of SEO optimization,
- on-page SEO,
- off-page SEO,
- SEO strategy.
- And so on … for all the topics you identified in step 1.
Use your Google Analytics, but also the Search Console, to find out which keywords you’re already ranking for.
This is not a final list of keywords that you will include on your website, but a generic list of keywords that you think users are searching for.
In the following steps, you will shorten and narrow that list and focus on the highest quality keywords.
3.3. Explore Related Keywords with Google Related Search Terms and Google Suggests
Now that you’ve cracked all the keywords you’ve had in your head, it’s time to take advantage of one of the few free tools and apps you can find on the web.
Type your keyword into a search engine and see what Google has to offer in its related search terms or using its Suggests mechanism.
3.4. Create a List of Basic Keywords and Long-tail Keywords
A quality keyword list consists of a combination of basic keywords (seed keywords) and long-tail keywords (long-tail keywords).
Basic keywords are shorter and more generic terms or phrases and consist of a maximum of 3 words.
Long-tail keywords are longer phrases that contain a keyword and consist of 3 or more words.
Why is it important to combine basic and long-tail keywords in your list?
Namely, basic keywords are searched more often, there is more competition for them and it is difficult to rank well for them.
On the other hand, long-tail keywords are easier to rank, and the traffic that comes through them is often of better quality, so you can see exactly what the audience is interested in.
3.5. Explore the Competition
If the competition is doing something, it does not mean that you should do it too. But knowing the keywords your competition wants to rank for can be of great help to you to check your list.
There is also a chance that your competitors have done extensive keyword research. Then why not take advantage of it? You can research the keywords they rank for and choose the best ones.
Does a competitor rank for the keywords you have on your list? Great, improve your rank just for them!
Ok, these are obviously the most popular keywords for which it will be the hardest to achieve the best result. But what about those keywords that your competition obviously cares less about? These keywords represent a special opportunity for you!
But even in this case, the balance is important – the balance between keywords for which there is a lot of competition and for which it is harder to rank and those keywords that are not so popular and represent a more realistic opportunity for success.
This balance is identical to that between basic and long-tail keywords – the goal is to create a list of keywords that will bring short-term success, but also have the potential for a long-term, more demanding result.
3.6. Reduce the List with Google Keyword Planner and Trends
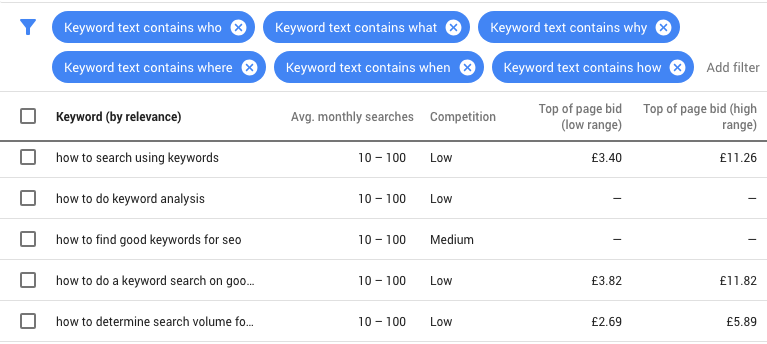
You have a fairly extensive keyword list, preferably a combination of the basic and long-tail keywords of the extremely popular ones and the slightly less popular ones.
There are two, of course, Google’s – Google’s keyword planning tool and Google Trends, the others are KeywordTool.io and MOZ’s, keyword researcher.
Use the Keyword Planner to test search training and estimate the traffic they can generate. Check which keywords they have according to (or far too many) searches that order balance in your slips. You can see similarities with the other, above-mentioned tools.
4. On-page SEO and Content Checklist
On-site optimization includes optimization of the following elements:
- URL
- Title tag
- Meta descriptions
- H tags (H1 to H6)
- Content and keywords
- Photos
- Internal links
- Website loading speed
- Mobile-friendliness
4.1. URL Structure in SEO
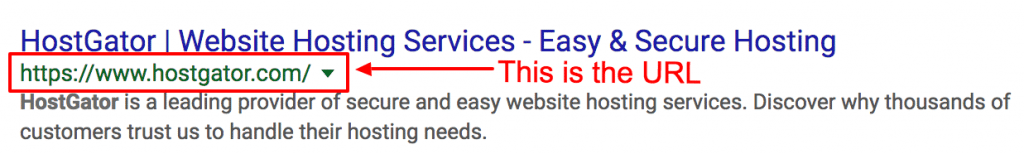 The URL is the website address. In order for a URL to be well optimized, it should not exceed 60 characters and should contain a keyword.
The URL is the website address. In order for a URL to be well optimized, it should not exceed 60 characters and should contain a keyword.
A well-optimized URL makes it easier for visitors to navigate the website and allows them to quickly understand exactly what category they are in within the site.
In addition, clear and concise URLs improve the architecture of a website and help it rank certain keywords in searches.
4.2. Title Tags
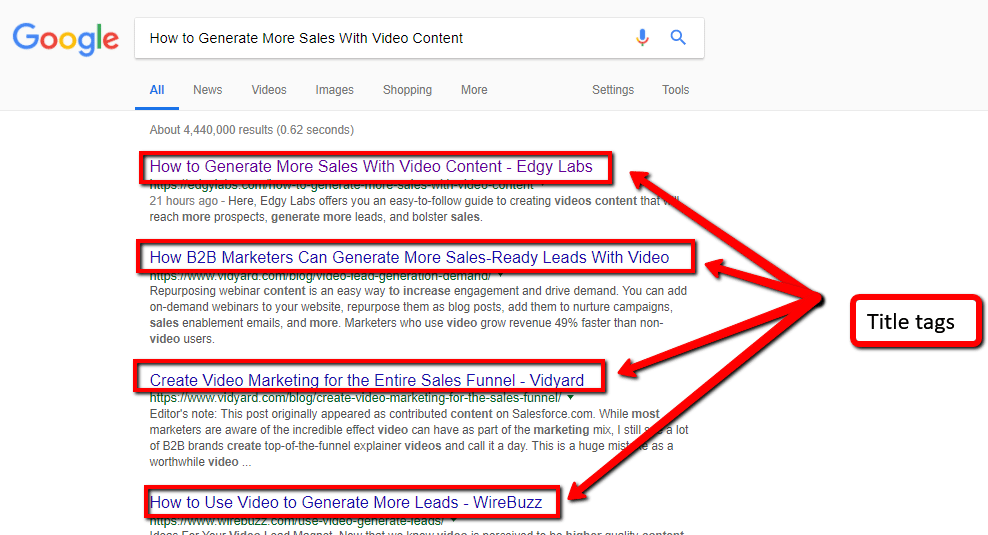 The title tag is the title of the web page that will appear in the search results.
The title tag is the title of the web page that will appear in the search results.
In order to display your website in search engine results (SERP), Google must first understand the subject matter of your website, and this job makes it easier for it to set the title tag correctly (<title> </title>).
The length of the title tag should not exceed 55 characters so that Google does not shorten it, and to make sure that the keyword will be displayed and visible, use it as close as possible to the beginning of the title.
4.3. Meta Descriptions
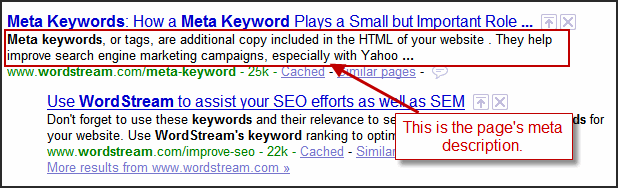 Meta descriptions do not have a direct impact on the ranking of a website on the SERP, but that does not mean that no attention should be paid to their optimization!
Meta descriptions do not have a direct impact on the ranking of a website on the SERP, but that does not mean that no attention should be paid to their optimization!
Namely, Google will bold the keyword within the meta description to show the user that the site has relevant information about the topic that the user is searching for, and a well-written meta description will attract more users than a meta description that is not well optimized.
As with the title tag, Google may shorten the meta description if it’s too long. Therefore, it is best to write meta descriptions no longer than 160 characters to make sure that the user will see the full text of the description.
4.4. Heading or H tags (H1-H6)
 Users do not like large and opaque blocks of text that make reading extremely difficult.
Users do not like large and opaque blocks of text that make reading extremely difficult.
To make reading web content easier and to easily divide it into smaller units, we use H-tags.
H tags are title tags within web content that help both Google and website visitors. Google uses H-tags to find out what the text is about, and H-tags help users read the content because they divide the content into smaller sections.
The most important step in optimizing H tags is to include the keyword in the H1 tag and use the H1 tag only once on each page.
You can use related keywords in other H tags, but make sure the text stays natural and legible. If, for example, H2 does not have the keyword you want to compete for, it is not harmful.
The goal is to make the text user-friendly and allow visitors to more easily find the information they are interested in.
4.5. Content and Keywords
Whether it’s a blog or a web store, content is what makes visitors come to your website. Well-optimized content involves writing original content with relevant and truthful information.
To make it easier for users to access this content, it is necessary to analyze keywords and use them in headings and paragraphs.
It is also important to pay attention to grammar and spelling and use multimedia (photos, videos, etc.) that will give users more context on the topic being discussed and make it easier to read and understand the text itself.
4.6. Photo Optimization
Photos are extremely important to website visitors for several reasons.
First, they break the monotony of the content and make it easier to read. In addition, they provide additional context to information within the text and make it easier to describe complicated processes or make it easier to describe products or services.
In addition to users, photo optimization is also important for Google. Namely, Google does not see the photo, but it does see its HTML information.
That’s why it’s important to add alt-attributes to help Google better understand what a photo represents.
4.7. Internal Links
 Internal linking of pages is often forgotten when talking about On-site SEO optimization, but it is extremely important for both visitors and Google.
Internal linking of pages is often forgotten when talking about On-site SEO optimization, but it is extremely important for both visitors and Google.
Google regularly crawls (passes) your website to find out if there is new content, a new page, or changes within the old content that need to be indexed and shown in the SERP in the future.
If you regularly place internal links, that is, links that lead from one page to another page within your website, Google will more easily recognize new and relevant pages and will better understand the context of the content of the page.
In addition to Google, internal links are also important for visitors, who will use such links to refer to additional sources within the website to provide them with more information and motivate them to stay longer on your website, thus increasing the conversion rate.
4.8. Website Page Speed
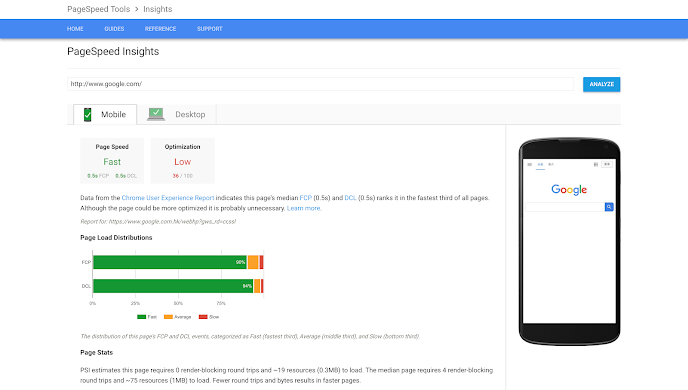 More than 50% of users will not wait more than 3 seconds to load a website. In order not to lose visitors and potential customers, optimizing the website page speed is extremely important.
More than 50% of users will not wait more than 3 seconds to load a website. In order not to lose visitors and potential customers, optimizing the website page speed is extremely important.
If you want to test the speed of your website, try a website speed test that will analyze the speed of your site and give you a rating and tips on how to speed up the page.
4.9. Mobile-friendliness
More than 50% of users search the Internet via tablets or smartphones, and that number is growing every day.
To enable these visitors to access information in the easiest way possible, Google has placed great importance on optimizing the website for mobile phones.
Namely, Google crawls (passes) the mobile version of your website and puts emphasis on it, and if your website is not optimized for smartphones or tablets, Google will not display it at the top of the SERP.
If you want to make sure your site is optimized for mobile phones as well, check out Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test tool.
5. Off-page SEO Checklist
Off-page SEO refers to everything that happens outside of our website, which increases the authority of the website on Google searches.

5.1. Elements of Off-page Optimization
When it comes to Off-page SEO optimization, it is most often about backlinks, that is, how to gather links from other websites that lead to your website.
So, Google is like a library that browses its database at high speed to provide the user with the book that will best answer the question. But how does Google know which website will give a user a quality response?
In addition to looking at On-page SEO signals such as page load speed, content, and keywords, links from other websites also help Google search.
If a lot of authors cite one book on a particular topic, it is very likely that the book is full of good and quality information.
Google uses the same principle – if a lot of websites link to one website, that website most likely has quality information and Google considers it more relevant than one website that does not have a single backlink.
Does this mean that it is easy enough to join a forum and paste a link to your website in the comment? Not! Such a practice is not desirable and Google rarely considers such links relevant.
5.2. The Number of Domains that Refer to You
100 links from one page and 100 links from 100 pages make a huge difference! This is quite logical – each website has its own audience.
So, if 100 different websites link to your website, the awareness of your website will increase and the number of visits to the website will increase.
In addition, if 100 pages send their visitors to your website, Google will understand that your website is high quality and useful and will reward you with better positioning on Google search results.
If you want to check how many different domains link to your website, use the free Ahrefs backlink checker.
5.3. Link Authority
Not all links are the same.
Namely, in addition to the previously mentioned number of domains that refer to your site, Google also looks at the quality of those websites.
Sometimes it is possible that your website will be linked by a website that is an absolute authority in your area so that link will be worth more than if you were linked to by a website that has just been created and has almost no authority on Google.
Of course, this does not mean that you should not be satisfied with these weaker links as well, because you are more likely to collect more such links than the number of strong links.
If you are interested in the authority of the website that links to you, use the Ahrefs tool for checking backlinks and below the UR section check the quality rating of the website, which is marked with a number from 1 to 100.
5.4. Follow or No-follow Links
Links can be “follow” or “no-follow”. These attributes refer to the HTML tag of the link, and the no-follow attribute actually tells Google to ignore that link, that is, such links do not transfer authority to the page they lead to.
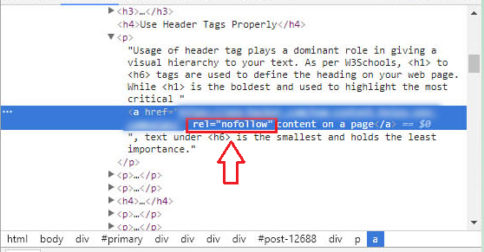
Such links are extremely easy to recognize. If the link does not have any tag in the HTML code, then it is a follow link, and no-follow is if it has a tag rel = “nofollow”.
5.5. Link Text
Anchor text refers to the text that appears on the web page instead of the text of the link itself. The link text is extremely important because it signals to the reader and Google in what context that link is mentioned.
Anchor texts are very useful in writing a blog because it will make it easier to motivate the reader to click on a link that will take him to another page within the same site or to another site that contains quality information related to a topic of interest to the user.
5.6. Link Relevance
Links are like votes for your website. So, if some website links to your website, it serves as a voice for your website.
Google counts these votes and considers those websites with the most votes and those with the best votes as authorities.
But not every vote is the same. The relevance of the link speaks to the thematic connection between the website that links and the website that the link points to.
Google appreciates the relevance of the link and, if another website with the same topic links to your website, Google will consider your website a source of quality information and will increase your search authority. For example, a link from a trusted tech blog to a page about SEO for cybersecurity will carry more value than a generic link from an unrelated niche.
Conclusion
From all this, we can conclude that SEO is a very important item nowadays. It is not the same whether your website is on the first or second page of a search engine. Better SEO will bring with it better ROI (Return on investment).
Well, and well-done SEO will certainly contribute to your better business and earnings.
It is very important that the content on the website is detailed, useful, and most importantly relevant to the selected keywords.
SEO optimization is not a one-time and easy job, but it is a marathon job in Internet marketing.
The rules change from year to year, and it is very important to follow all the trends and algorithms to make the position of the website as good as possible.

Comments are closed.